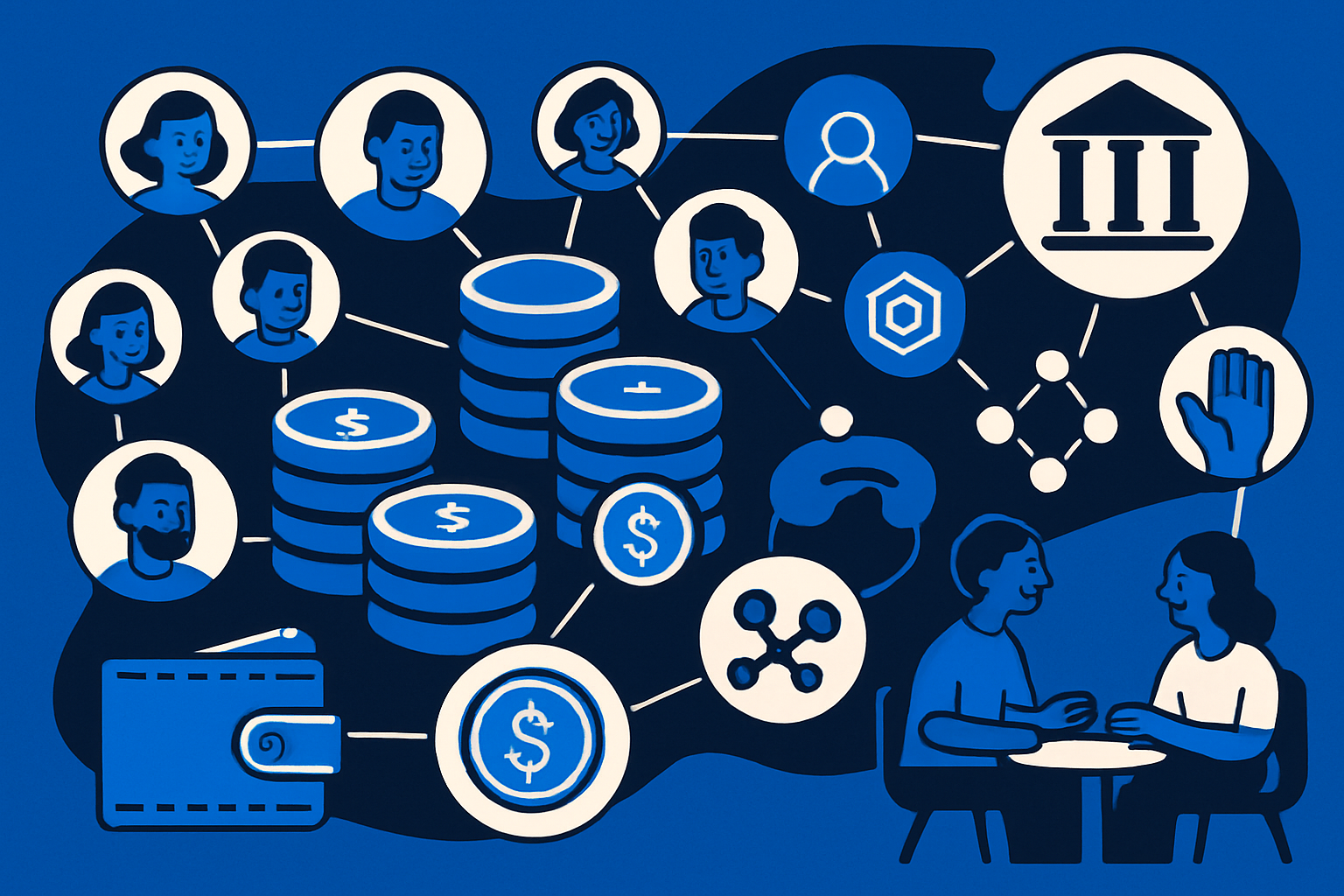
In 2025, the regulatory landscape for stablecoins is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the adoption of Compliance as Code across major jurisdictions. This paradigm shift is not just technical – it is fundamentally reshaping how regulators, issuers, and service providers interact with the fast-evolving world of digital assets. By encoding legal requirements directly into smart contracts and transaction logic, Compliance as Code promises both efficiency and rigor in an industry where manual processes have long struggled to keep pace with innovation.

How Compliance as Code Works: From Legal Text to Machine-Readable Rules
The core idea behind Compliance as Code is deceptively simple: translate complex regulatory requirements into machine-readable code that operates autonomously within digital asset ecosystems. For stablecoins, this means embedding rules for KYC (know your customer), AML (anti-money laundering), reserve management, and reporting directly into the protocols that govern issuance and transfers.
This approach offers several clear advantages:
Key Benefits of Compliance as Code for Stablecoin Regulation
-

Automated Regulatory Enforcement: Compliance as Code embeds regulatory requirements directly into stablecoin platforms, ensuring that every transaction and process adheres to laws such as the GENIUS Act (U.S.) and MiCA (EU) without manual intervention.
-

Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: Systems can continuously monitor transactions for compliance, providing instant alerts and generating audit trails required by regulators like the U.S. Treasury or European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
-

Reduced Human Error and Operational Risk: By automating compliance checks, the risk of manual mistakes—such as incomplete KYC or reserve miscalculations—is significantly lowered, supporting the strict reserve and identity mandates seen in Hong Kong and Singapore.
-

Scalability Across Jurisdictions: Compliance as Code allows stablecoin issuers to adapt quickly to new or updated regulations in multiple regions, facilitating global operations while maintaining regulatory alignment.
-

Enhanced Transparency and Auditability: With compliance logic codified, regulators and auditors can easily verify that stablecoin issuers meet requirements for reserve backing, transaction reporting, and customer protection as mandated by frameworks like GENIUS Act and MiCA.
For example, under the U. S. GENIUS Act, stablecoin issuers must maintain 1: 1 reserves in high-quality liquid assets and comply with robust reporting standards. With Compliance as Code, these obligations are enforced automatically, transactions that would breach reserve ratios or bypass KYC checks are programmatically blocked at the protocol level.
The United States: GENIUS Act Sets a New Standard
The Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U. S. Stablecoins (GENIUS) Act, signed into law on July 18,2025, marks a watershed moment for American crypto regulation. For the first time, there is a unified federal framework specifically tailored to payment stablecoins. Key provisions include:
- Mandatory 1: 1 Reserves: Issuers must fully back every token with specified liquid assets.
- Bank Secrecy Act Compliance: Automated transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting are now built into most compliant systems.
- Securities Clarity: Stablecoins meeting GENIUS criteria are expressly exempt from securities or commodities classification.
This regulatory clarity has spurred rapid adoption of machine-readable compliance routines within U. S. -domiciled stablecoin projects. The act’s explicit support for automated compliance tools has triggered a wave of investment in RegTech solutions that encode everything from customer onboarding to real-time reserve audits.
Europe and Asia: Divergent Approaches to Automated Stablecoin Oversight
The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA), which became fully effective in December 2024, takes a similarly rigorous but distinct approach to jurisdictional stablecoin compliance. MiCA requires all issuers of electronic money tokens (EMTs) or asset-referenced tokens (ARTs) to implement automated segregation of client funds and periodic disclosure routines, features now commonly coded directly into smart contract architectures.
Asia’s leading financial centers are also innovating on compliance automation. Hong Kong’s new law mandates identity verification for every token holder at both issuance and transfer stages, an unprecedented level of KYC scrutiny enabled by integrating real-time checks into wallet software and transfer protocols. Singapore continues its push for machine-enforced reserve audits under its own framework established in late 2023.
Jurisdictions Leading Machine-Readable Crypto Regulation in 2025
-

United States: GENIUS Act 2025 — The U.S. pioneered machine-readable stablecoin regulation with the GENIUS Act, signed in July 2025. This act mandates automated compliance checks, 1:1 reserve backing in high-quality liquid assets, and direct integration of regulatory logic into stablecoin codebases, setting a new standard for compliance automation.
-

European Union: MiCA Enforcement — The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) became fully effective in December 2024, requiring stablecoin issuers to embed regulatory controls—such as reserve verification and anti-money laundering checks—directly into their systems. MiCA’s machine-readable compliance mandates are now industry benchmarks across the EU.
-

Hong Kong: Stablecoin Ordinance 2025 — Hong Kong’s new stablecoin law, effective August 2025, requires issuers to implement automated KYC and identity verification for every token holder. This regulation leverages compliance as code to ensure real-time adherence to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing standards.
-
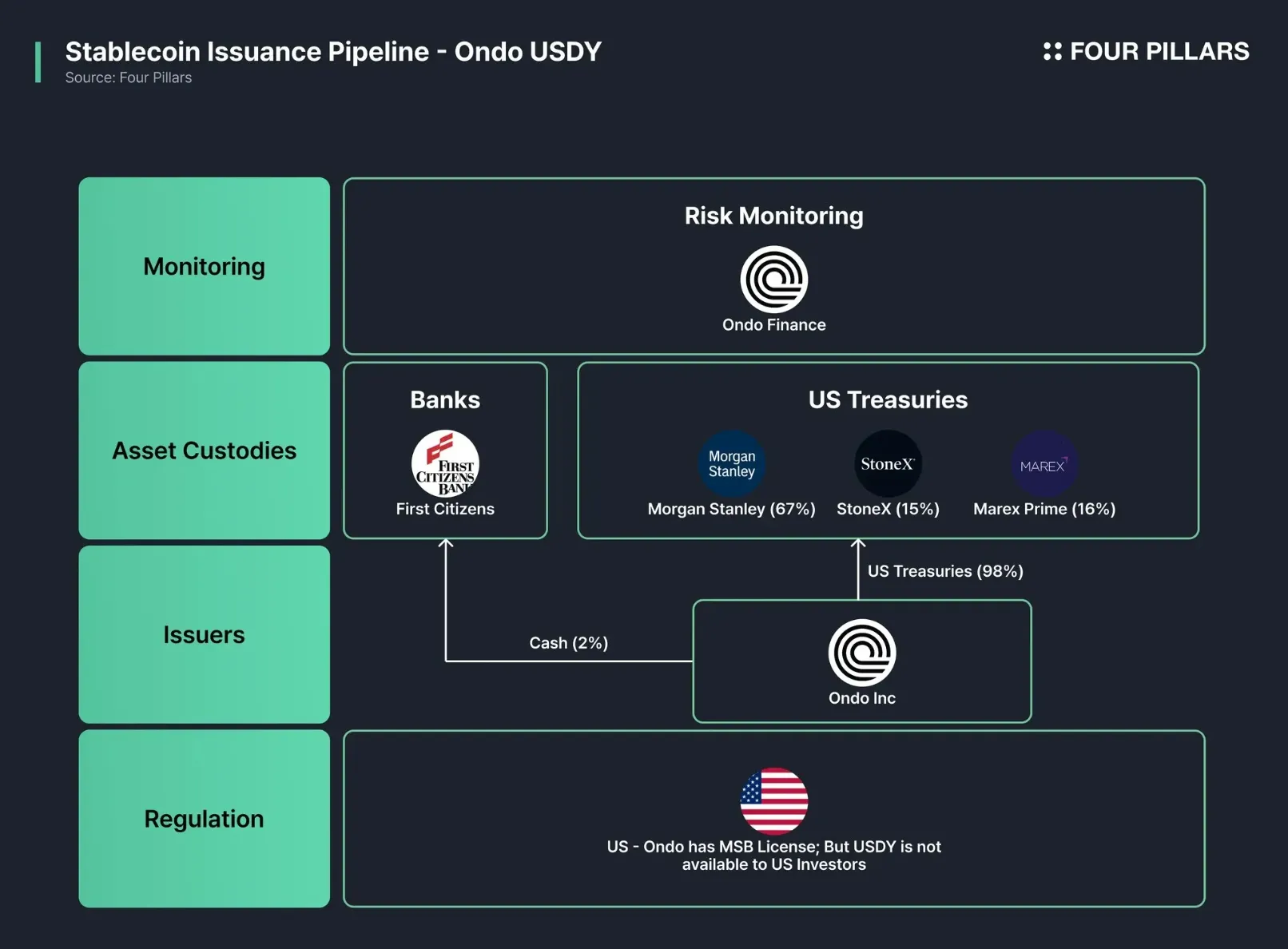
Singapore: Stablecoin Regulatory Framework — Singapore’s regulatory regime, building on its 2023 framework, mandates that stablecoin issuers use machine-readable compliance mechanisms for reserve management and transaction monitoring. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) enforces these requirements to ensure transparency and systemic stability.
The Technical Challenges Ahead
Despite these advances, implementing true Compliance as Code remains technically complex. Regulatory language is often ambiguous or subject to interpretation; translating statutes into unambiguous code requires close collaboration between legal experts and developers. There are also unresolved questions about privacy, especially where KYC data must be processed on-chain, raising tension between transparency demands and individual rights.
The next wave of innovation will likely focus on privacy-preserving compliance mechanisms such as zero-knowledge proofs or off-chain attestations that satisfy regulators without exposing sensitive user data on public ledgers.
Meanwhile, regulators and industry groups are collaborating to develop standardized protocols and open-source libraries for compliance logic. These efforts aim to reduce fragmentation and ensure that machine-readable rules remain up to date as laws evolve. The emergence of regulatory sandboxes in the U. S. , EU, and Asia is also accelerating the testing and refinement of automated compliance modules before they are deployed at scale.
The rise of stablecoin regulatory technology is making it increasingly feasible for both startups and established institutions to launch compliant products across multiple jurisdictions. By leveraging modular codebases, issuers can adapt their compliance stack to local requirements, switching between GENIUS Act, MiCA, or Hong Kong’s identity mandates, with minimal friction. This flexibility is essential as global stablecoin regulation in 2025 continues to fragment along regional lines.
Opportunities and Risks: Harmonization vs. Regulatory Arbitrage
While Compliance as Code offers a path toward harmonized oversight, it also introduces new vectors for regulatory arbitrage. Issuers may be tempted to deploy code that meets the letter but not the spirit of local laws, or exploit gaps between machine-enforced standards in different regions. As highlighted by recent enforcement actions in both the U. S. and Asia, regulators are watching closely for attempts to circumvent reserve requirements or KYC obligations via technical loopholes.
To address these risks, some jurisdictions are moving toward mutual recognition agreements and cross-border audits of compliance codebases. The goal is to prevent a race-to-the-bottom while preserving innovation, a delicate balance that will define the next phase of stablecoin adoption.
The Path Forward: Best Practices for Issuers
For market participants navigating this new environment, several best practices are emerging:
Key Steps for Stablecoin Compliance in 2025
-

Map Applicable Jurisdictional Regulations: Identify and analyze the latest stablecoin regulations in each target jurisdiction, such as the GENIUS Act (U.S.), MiCA (EU), and Hong Kong’s Stablecoin Law. Ensure your compliance program addresses the unique requirements of each framework.
-

Integrate Compliance as Code: Embed regulatory requirements directly into your stablecoin’s smart contracts and operational systems. This enables automated, real-time compliance with laws like 1:1 reserve mandates, KYC, and AML standards across jurisdictions.
-

Establish Robust Reserve Management: Maintain 1:1 reserves in high-quality liquid assets as mandated by the GENIUS Act and MiCA. Implement transparent, auditable systems for real-time reserve verification and segregation of customer funds.
-

Implement Comprehensive KYC/AML Procedures: Enforce stringent KYC and AML checks for all users, aligning with requirements such as Hong Kong’s identity verification rules and EU AML directives. Automate these processes using secure, privacy-conscious solutions.
-

Obtain Required Licenses and Registrations: Register as a permitted payment stablecoin issuer (U.S.), electronic money institution (EU), or equivalent in each jurisdiction. Ensure ongoing compliance with licensing conditions, including periodic reporting and audits.
-
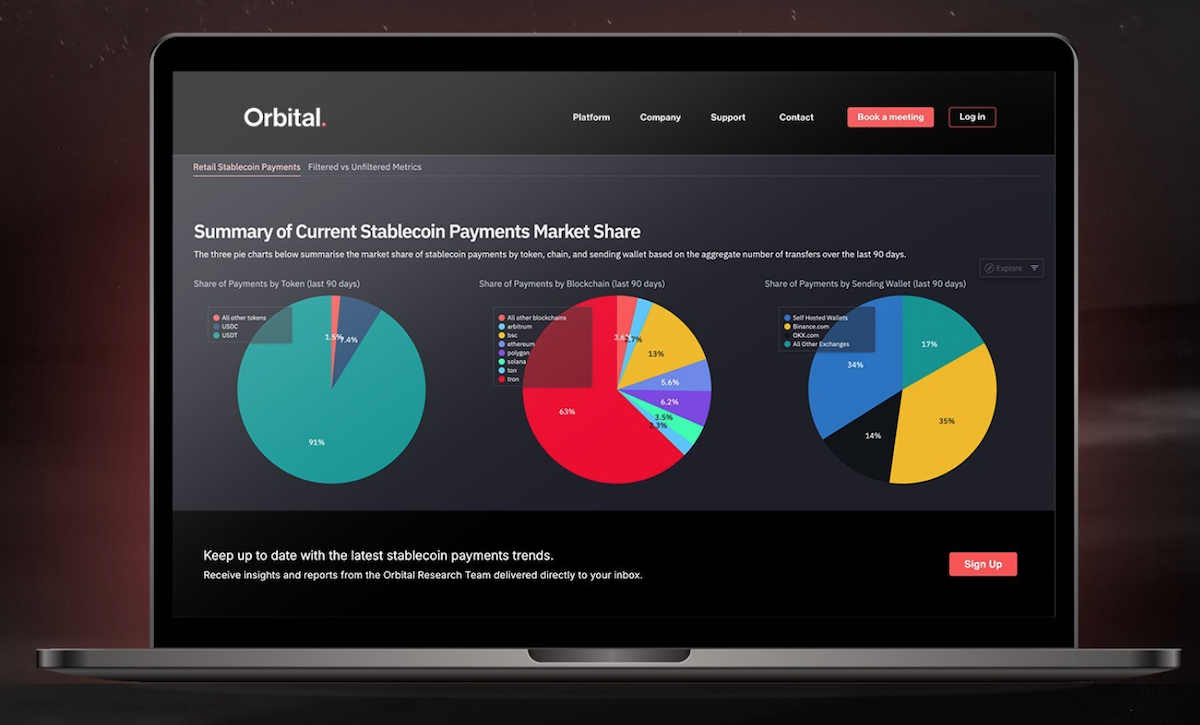
Establish Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: Deploy systems for continuous compliance monitoring and automated regulatory reporting. This supports early detection of non-compliance and streamlines interactions with regulators.
-
Address Data Privacy and Security: Design compliance solutions that protect user data and comply with privacy laws such as the GDPR in the EU and local data protection acts in Asia. Balance transparency with robust data security measures.
Staying current with evolving standards is non-negotiable; automated systems must be continuously updated as new guidance emerges from bodies like the U. S. Treasury or European Banking Authority. Engaging legal counsel with expertise in multi-jurisdictional digital asset law can help avoid costly missteps during implementation.
The trajectory is clear: machine-readable regulation will become the norm rather than the exception in digital finance. As stablecoins move deeper into mainstream payment rails and institutional portfolios, only those projects that invest early in robust Compliance as Code infrastructure will remain viable, and trusted, partners.
The convergence of law and software isn’t just a technical upgrade; it’s a fundamental redefinition of how trust is engineered in financial markets.






